This lesson will illustrate quite a simple concept – relative position of two circles. That is, to find whether two circles, with known centres and radii, lie completely outside one another, touch each other, intersect at two points, or are such that one lies inside the other.
For all these cases, consider two circles, with centres C1 and C2, and radii r1 and r2 respectively.
Two circles touching each other externally
I’ve talked a bit about this case in the previous lesson. Take a look at the figure below.
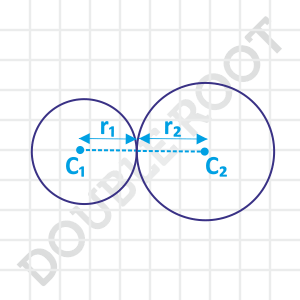
We have two circles, touching each other externally. And it’s pretty obvious that the distance between the centres of the two circles equals the sum of their radii. That is, C1C2 = r1 + r2, which will the required condition for two circles to touch each other externally. Makes sense?
Two circles lying outside each other
In the previous case, what if we move one of the circles slightly away from the other? The two circles will not touch each other anymore, and lie outside each other.
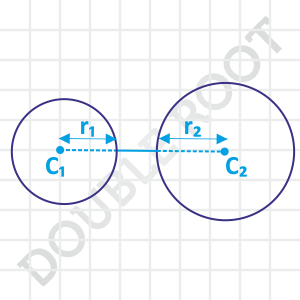
Since by separating them, we’ve increased the distance between their centres, the distance C1C2 will become greater than r1 + r2. Therefore the required condition will be C1C2 > r1 + r2
Two circles touching each other internally
Have a look at the figure.
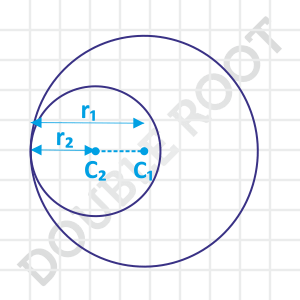
In this case, the distance between the centres equals the difference of the radii of the circles, i.e. C1C2 = r1 – r2. Do you see it?
One circle lying inside another
Now let’s push the smaller circle a bit towards right, making it lie completely inside the larger circle.
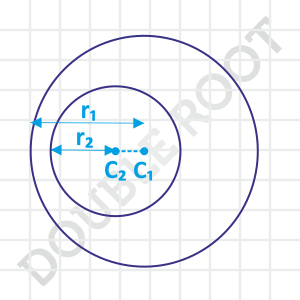
While shifting the circle, we’re making C1C2 smaller than what it was in the previous case. That means, the required condition for this case will be C1C2 < r1 – r2.
Two circles intersecting each other at two points
Consider the third case again. What if we pushed the smaller circle towards the left? (Or the larger to the right?). The circles will now intersect at two points. And, we’re now increasing the distance between their centres, implying C1C2 > r1 – r2.
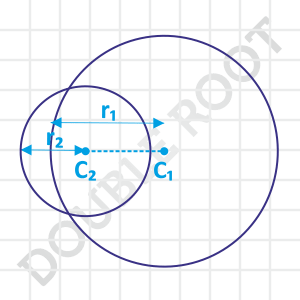
But we cannot push it indefinitely towards the left, because a situation would arise when C1C2 will become equal to r1 + r2, and the circles will touch each other again, but externally. That means, if we want the circles to intersect at two points, we’ve to keep the distance between their centres less than the sum of their radii.
Considering all this, we get the required condition for this case as r1 – r2 < C1C2 < r1 + r2
Notice that in the last three cases, I’ve assumed that r1 > r2 (otherwise r1 – r2 would come out to be negative). For any two given circles, you can always assume the larger radius to be r1, or alternatively, you can use the absolute value of their difference.
And that’s all about relative position of two circles. I hope that was pretty easy to understand.
Lesson Summary
I’ve summarised the lesson in the following table:
Position |
Condition |
Lying outside each other |
C1C2 > r1 + r2 |
Touching externally |
C1C2 = r1 + r2 |
Intersecting at two points |
|r1 – r2| < C1C2 < r1 + r2 |
Touching internally |
C1C2 = |r1 – r2| |
One lying inside other |
C1C2 < |r1 – r2| |
In the next lesson, I’ll take up a few examples to demonstrate these cases.